Digital Forensics
Introduction
What is digital forensics?
Digital forensics is generally known as the application of computer science to process data while preserving the integrity of the electronic information. Digital forensics is the extension of its predecessor "computer forensics" after the evolution of digital media allowed for several of new types of devices to store digital data. With several techniques available, the main focus is often to recover and investigate the material found in electronic devices.
Digital investigators use different techniques in the forensic process to gather potential evidence for the purpose of preservation, extraction and presentation of evidence. Digital evidence is most commonly used to support or refute cases in a court of law but is also seen in the private sector to support internal investigations or corporate disputes.
What is electronic information?
Electronically stored information (better known simply as "data") is information that has been created, altered, communicated or stored in a digital form. Digital investigators retrieve information from a variety of sources and file systems (FAT, NTFS HFS etc.) and with the exponential increase in digital information being created and stored each day, it is important to have systems in place to efficiently handle these large quantities of data.
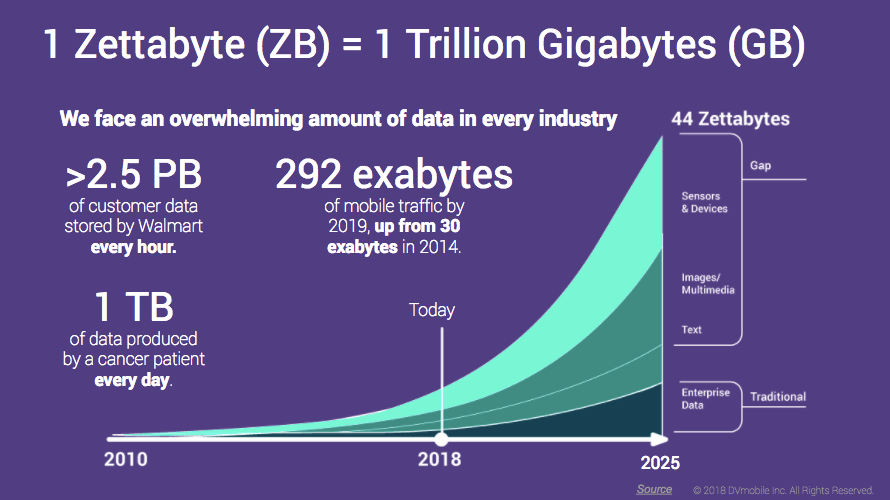
Source: https://www.gregverdino.com/everything-is-exponential/
The information we are looking for may not always be directly accessible to the digital investigator. The way we store data is also changing with the way we move from physical documents and cabinets over to more convenient methods such as local servers and cloud services. Cloud services in particular raised new challenges relating to ownership of data and international jurisdiction of the stored files.
Through software and techniques, data may be accessible even if deleted by the owner and reconstructed. Other challenges relating to accessing digital information may include concealment of a file within another file (steganography) or making files inaccessible through encryption or remote cloud locations with limited or restricted access. Distributed ledger technologies are also known to have been used for communication, making it difficult to trace and locate relevant information in an anonymous network. The most commonly seen types of electronic media are in the form of different types of hard disk drives, smart phones, USB drives, memory cards and optical media.